
1° structure
Primary Structure : the sequence of bases along the pentose-phosphodiester backbone of a DNA molecule.
- Base sequence is read from the 5’ end to 3’ end
- System of notation single letter ( A, G, C and T )
2° Structure
Secondary Structure : the ordered arrangement of nucleic acid strand
- The double helix model of DNA 2° structure
- Double helix : two antiparallel poly nucleotide strands are coiled in a right-handed manner about the same axis.
Base Pairing
- Base pairing is complimentary
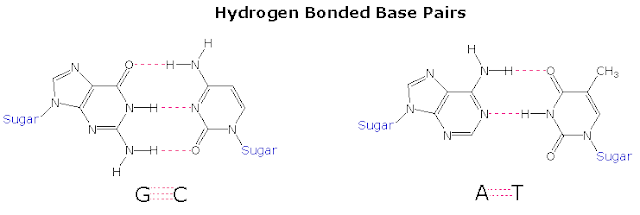
- A major factor stabilizing the double helix is base pairing by hydrogen bonding between T-A and between C-G
T-A base pair comprised of 2 hydrogen bonds
G-C base pair comprised of 3 hydrogen bonds
3° Structure
Tertiary Structure : the three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms of nucleic acid (supercoiling)
- If the DNA is twisted in the direction of the helix, it is said that the positive supercoiling, and the bases are held together more closely.
- If the DNA is twisted in the opposite direction is called negative supercoiling, and away basis. In nature, most DNA has slight negative supercoiling that is produced by enzymes called topoisomerases.
4° Structure
Quaternary Structure : The structure of chromatin
- Each ‘bead’ is a nucleosome. Nucleosome consist of DNA wrapped around histone core.
- Histone : a protein, found associated with eukaryotic DNA
- Chromatin : DNA molecules wound around particles of histones in a beadlike structure.










No comments:
Post a Comment